Greenland – a current and prospective geostrategic issue – Maritime Security Forum Analysis
As the largest island territory in the world, Greenland is located in the Northwest Atlantic and is administered by the Kingdom of Denmark. With a small population and low density, the territory is known for its glacial landscapes and unique ecosystem. In recent years, Greenland has become a subject of growing interest due to climate change and its impact on the region.
Greenland (in Greenlandic Kalaallit Nunaat – ‘Land of the People‘, in Danish Grønland – ‘Green Earth‘), geographically Greenland is an autonomous territory, part of the Kingdom of Denmark, with county status.
Source: Google.maps
In 1814, when Norway was separated from Denmark after the Napoleonic Wars, the colonies, including Greenland, remained under Danish control. During World War II, Greenland broke away from Denmark (then under German occupation), both economically and socially, and moved closer to the United States and Canada. After the war, the island returned to Danish control and, in 1953, its colonial status was changed to that of an overseas Amt (county). In 1985, Greenland, following a referendum, left the European Community, which it joined in 1973 as part of Denmark. Negotiations for full independence also began.
There is still a territorial dispute with Canada over sovereignty over Hans Island.
On November 26, 2008, a referendum was held in Denmark on the island’s self-determination, with 75.5% in favor.
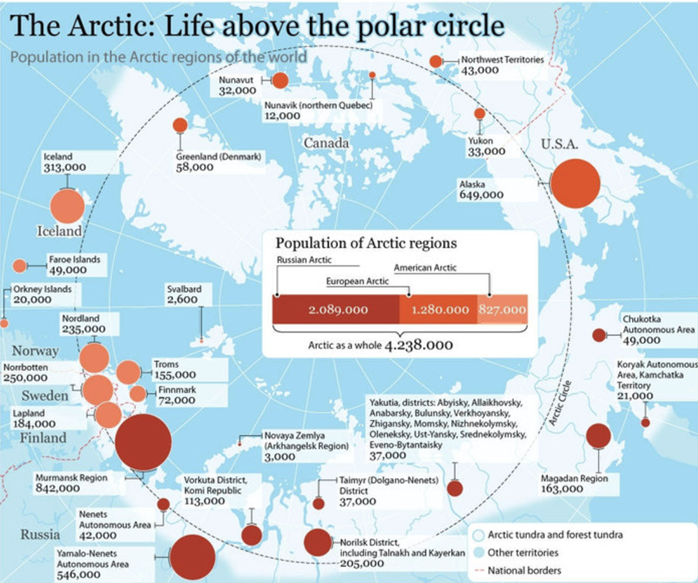
Source: https://russiancouncil.ru/en/analytics-and-comments/analytics/nato-and-a-new-agenda-for-the-arctic/
This growing interest is fueled by the recognition of Greenland’s strategic role in global geopolitics and its abundant natural resources, which are becoming increasingly valuable in the context of climate change. This recognition also underlines Greenland’s strategic importance as an access point to emerging maritime routes and as a base for resource exploration and exploitation activities.
In addition, Greenland becomes a key player in international disputes over maritime and territorial resource rights. This is due to Greenland’s strategic position close to key sea routes and significant natural assets, which are becoming increasingly important in the context of climate change and global competition for resources.
Climate change is causing rising temperatures in the Arctic, thus providing opportunities for year-round use of sea passages, which substantially reduces the distances between China, Western Russia, Europe and the North American continent.
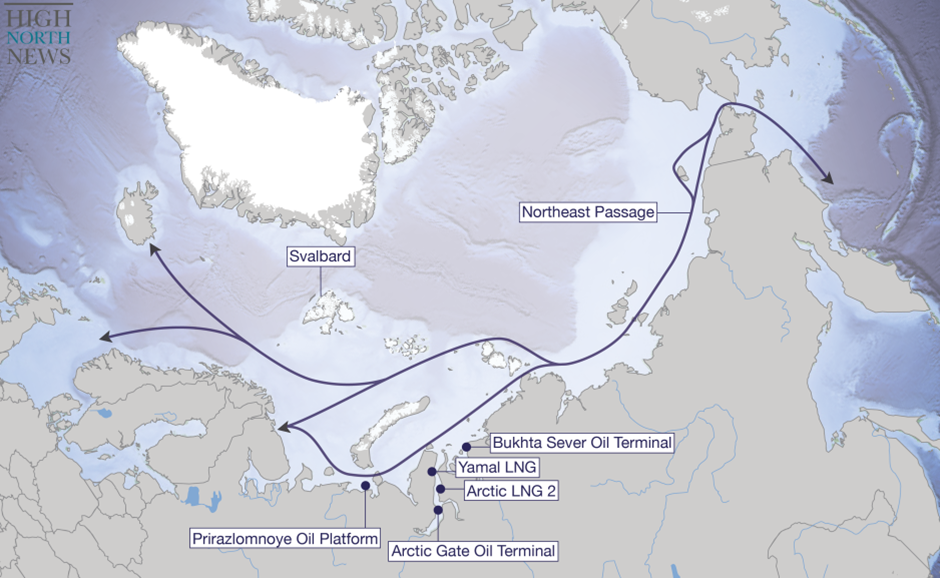
Source: https://www.highnorthnews.com/en/ukraine-arctic-russias-capabilities-region-and-wars-impact-north
Source: Wikipedia
Geographical and historical background
Strategically located between the North Atlantic and the Arctic Ocean, Greenland occupies a significant geographical position. With a history stretching from early Inuit and Nordic settlers to Danish colonization, the territory has a rich historical legacy. Today, Greenland’s limited autonomy, but also its natural resources and economic potential are fundamental elements in the territory’s geographical and historical context.
This underlines Greenland’s strategic importance in international relations, given its privileged geographical position between North America and Europe. This geographical position makes it a point of interest not only for the states in the region, but also for those seeking to extend their influence over natural resources and trade routes.
Its geographical position makes it a point of interest not only for states in the region, but also for those wishing to extend their influence over natural resources and trade routes.
Another perspective
Greenland, situated between North America and Europe, has always been a battleground between global powers, given the mineral wealth and freshwater resources it offers. This geographical position made Greenland an important strategic point during the Cold War, when the United States and the Soviet Union increased their influence in the region.
Greenland has also been a center of interest for climate change research, as the melting of its glaciers may have significant global implications. These changes may influence not only local ecosystems but also ocean circulation and global climate. In addition, Greenland has an important geostrategic position with abundant natural resources, including minerals and hydrocarbons, which attract international interest.
Natural resources and economic potential
Greenland has impressive natural resources of strategic importance in the global economy. It has considerable reserves of rare metals, including neodymium[1], praseodymium[2] and dysprosium[3], which are essential in modern technology industries. The country also has deposits of gold, uranium, diamonds, lead, zinc and other precious minerals. These resources attract the interest of international mining companies, contributing to Greenland’s economic potential and to the development of global commodity markets.
In this context, Greenland enjoys a favorable geo-strategic position, which makes the exploitation of these resources not only profitable, but also essential for the sustainable economic development of the region.
These resources include valuable minerals, freshwater resources and the energy potential of coastal areas. Greenland also has significant reserves of oil and natural gas, which are becoming increasingly accessible due to climate change and melting glaciers. This not only attracts international investors, but also increases Greenland’s strategic importance on the global economic map. This is essential for the development of the region’s infrastructure and natural resources, such as rare minerals, which are increasingly sought after worldwide.
Mineral resources
Greenland’s mineral resources are of particular importance in the context of the global dependence on such resources. Greenland has, for example, among the world’s largest reserves of neodymium and praseodymium, which are essential in the production of technological equipment. The country also has considerable resources of gold, uranium, diamonds, lead, zinc and other precious minerals.
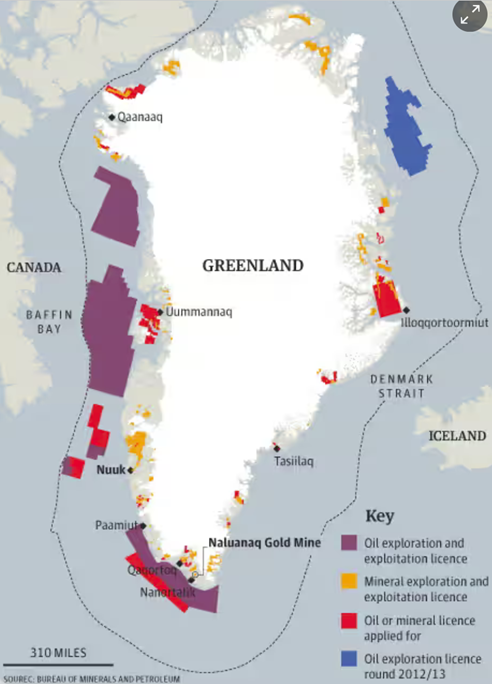
Source: The Guardian
Greenland’s rich potential is generating interest in the international mining industry and has a significant impact on the global economy. It attracts foreign investment and spurs local infrastructure development, and access to these resources can turn Greenland into a key player in the global minerals market. This will not only enable economic growth, but also better integrate Greenland into international supply chains, thus increasing its geopolitical influence.
It will also make it easier to attract foreign investment and stimulate the development of the infrastructure needed to exploit these resources. In addition, access to mineral resources will provide Greenland with opportunities for international collaboration, especially with countries that have an interest in the raw materials essential to their industries. These collaborations could lead to the development of joint projects, thereby stimulating the local economy and attracting foreign investment.
Access to mineral resources could also enable Greenland to become a key player in the global raw materials market. This could make it easier to attract foreign investment and international collaborations, thereby strengthening the local economy. This could attract international companies interested in exploiting these resources, with a significant impact on infrastructure development and job creation in Greenland.
International geopolitical interests
Greenland has some of the world’s largest mineral resources, making it a strategic point of interest for several countries. In addition, from a military point of view, control over the territory can provide the power to control Arctic sea routes and ensure regional security.
These issues are key to maintaining influence over the abundant natural resources in the area, such as hydrocarbons and rare minerals, which are becoming increasingly valuable as climate change opens up new shipping routes. These resources are essential for the economic and military development of the nations concerned, as Greenland is strategically located between North America and Europe.
Moreover, competition for access to these resources may lead to heightened international tensions as global powers review their security and cooperation strategies in the region. This competition may provoke not only direct confrontation, but also a reassessment of traditional alliances, particularly in the context of intersecting international geopolitical interests in the Arctic.
This reassessment could lead to the formation of new power blocs, in which international actors such as the United States, Russia and China will increase their influence in the region. Greenland’s abundant natural resources, including minerals and natural gas, will also attract the attention of major economies seeking to expand their access to essential raw materials.
Not only will these resources contribute to Greenland’s economic development, but they will also influence international relations, leading to fierce competition between countries seeking to secure access to these riches.
In addition, Greenland’s geographically relevant position allows it to serve as a strategic vantage point on the Northern Sea Route and will increase its importance in the global geopolitical context.
US and NATO
The US has shown an increased interest in Greenland from an economic as well as a military perspective, given the territory’s strategic geographic position. NATO also seeks to strengthen its presence in the region to ensure collective security and to counter the growing influence of other international actors in the area.
This strategy is essential to prevent geopolitical destabilization of the region and to protect the alliance’s economic and strategic interests. In this context, the US and NATO must work closely together to ensure Greenland’s security, given its strategic position in the Arctic, which is becoming increasingly important in the face of climate change and international competition for natural resources. This partnership is essential to counter emerging threats in the area, such as aggressive military activities by other nations.
Collaboration between the US and NATO will also facilitate the development of effective defense and resource management strategies, ensuring a coordinated response to geopolitical challenges. This collaboration is essential for strengthening security in the Arctic region, given Greenland’s abundant natural resources and its strategic importance in the context of geopolitical rivalries between major powers. In this context, collaboration between the US and NATO is becoming a crucial factor in ensuring stability and security in this strategic area, particularly in view of emerging challenges from other states such as Russia. This collaboration is based on common interests in the maintenance of peace and security, as well as on the collective defense commitments stipulated in Article 5 of the NATO Treaty. It is also essential for the US to strengthen its military presence in Greenland, given its strategic location close to important sea routes and natural resources.
Greenland could be viewed as a strategic buffer zone, especially if the Pentagon deploys air defense (AD) systems. The positioning of these systems could give the US a defensive advantage against ballistic missiles launched from Russia.
This dynamic underscores Greenland’s geostrategic importance in global conflicts and North American defenses.
The Arctic remains central to NATO’s deterrence and defense posture.
Climate change and its impact on Greenland
Greenland is strongly affected by climate change, with rising temperatures and accelerated melting of glaciers leading to rising sea levels. These changes are having a major impact on the ecosystem, biodiversity and the way of life of the inhabitants. At the same time, melting glaciers lead to the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, contributing to global warming and climate change around the world. This, in turn, can affect fragile ecosystems in the region and lead to a rise in sea levels, which could have devastating consequences for coastal communities. These changes may cause species migration and significant disruption of food webs, which will increase the region’s vulnerability to other environmental threats. These impacts will affect not only local biodiversity but also the economic activities of communities that depend on Greenland’s natural resources.
Melting glaciers and sea level
Melting glaciers in Greenland have a significant impact on sea level. It is now estimated to be contributing about half a millimetre per year to global sea level rise. This continued rise is threatening coastal areas around the world with serious consequences for local communities and biodiversity.
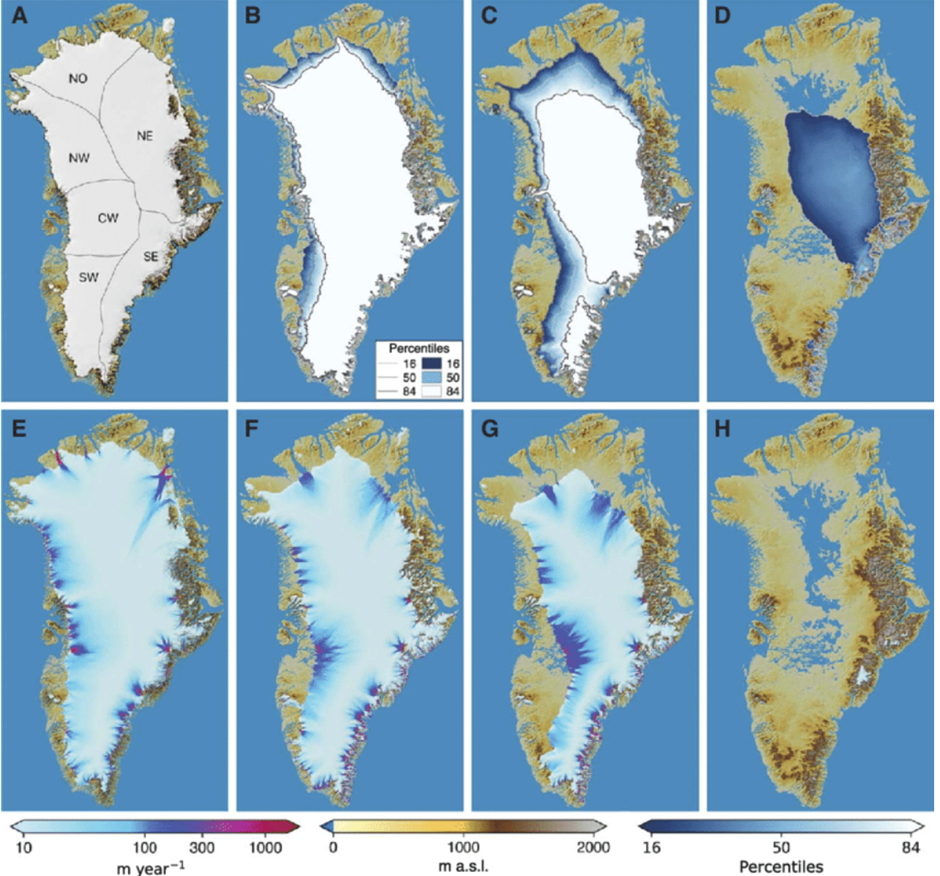
The observed state since 2008 and simulations of the Greenland ice sheet in the year 3000. (A) Observed ice extent in 2008 (53). (B to D) Probability (percentiles) of ice-sheet as a percentage of the ensemble simulations with non-zero ice thickness. Probabilities lower than the 16th percentile are masked. (E) Multi-year composite of observed surface velocities (61). (F to H) Surface velocities from the control simulation. Basin names shown clockwise in (A) are southwest (SW), center-west (CW), northwest (NW), north (NW), north (NO), northeast (NE), and southeast (SE). RCP 2.6 (B and F), RCP 4.5 (C and G), and RCP 8.5 (D and H). Topography in meters above sea level (m a.s.l.) [(A) to (H)].
Source: Researchgate
It has also been observed that the melting of Greenland glaciers may also affect global ocean circulation, with the potential to change global climate patterns.
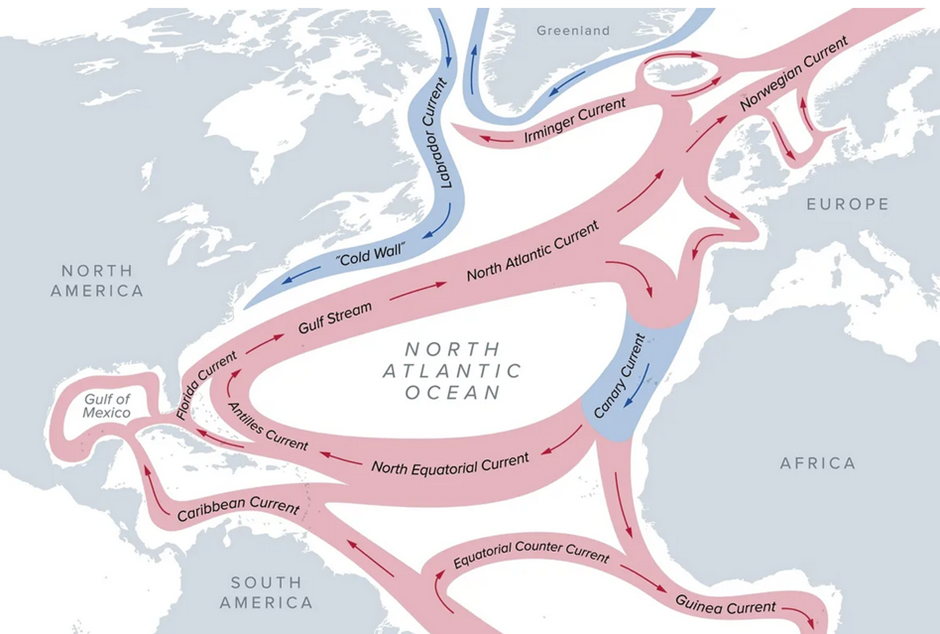
This change may lead to a redistribution of heat in the world’s oceans, affecting the weather and climate of many regions. In addition, melting glaciers are contributing to rising sea levels, threatening coastal areas and the communities that depend on them. This has serious implications not only for marine ecosystems but also for the local economy, which depends on the resources available in coastal areas.
Melting glaciers are also contributing to rising sea levels, which can lead to coastal erosion and flooding of coastal communities. These climate changes not only affect the natural landscape, but also jeopardize economic activities such as fishing and tourism, which are essential for the survival of local communities.
5. Conclusions and future perspectives
In conclusion, Greenland has significant economic potential due to its natural resources, especially mineral resources.
With increasing international geopolitical interests and climate change underway, it is clear that Greenland will become an increasingly important player in the global landscape.
In the future, it is essential that the Greenland Government takes measures to protect the environment and make sustainable use of resources for sustainable and responsible economic development. These measures should include the promotion of renewable energy, the conservation of biodiversity and the involvement of local communities in decision-making.
It is also important for Greenland to work together with other states to tackle the global challenges of climate change, thus ensuring a better future for generations to come. This collaboration will enable the development of effective strategies to manage natural resources, protect biodiversity and reduce carbon emissions. These initiatives will help to strengthen the local economy and create sustainable jobs in Greenland, while promoting an environmentally friendly development model. These initiatives will help to strengthen the local economy and create sustainable jobs in Greenland, while at the same time promoting an environmentally friendly development model.
In conclusion, it is essential that these strategies are implemented with a strong focus on international collaboration, given Greenland’s strategic importance in the current geopolitical context. This collaboration will not only strengthen relations between nations, but will also contribute to the stability of the Arctic region, as Greenland plays a crucial role in energy security and global climate change. In this context, it is essential that countries work together on research and development of green technologies that can reduce the impact of climate change. Strategic partnerships in infrastructure and natural resources will also ensure a sustainable development of the region, given Greenland’s considerable economic potential.
Bibliography
1. M Bușe – Bulletin of the National Defense University “Carol I”, 2021 – ceeol.com. ARCTIC ZONE, EUROPEAN UNION AND CLIMATE CHANGE AS A GLOBAL SECURITY THREAT. unap.ro
2. G Teodorescu – researchgate.net. 1.5. Sustainable development in an institutional context – Case study, University “Valahia” of Targoviste in the UI GreenMetric Ranking …… researchgate.net
3. S Pencea, AC Bâlgăr – … of Global Economics/Journal of …, 2023 – search.ebscohost.com. CHINA’S MINERAL RESOURCE STRATEGIES CRITICAL TO FUTURE TECHNOLOGIES … [HTML].
4. APCCC ROGOZAN, ICICS LEARSCHI LEARSCHI – 2023 – academia.edu. ROMANIA’S MARITIME RESILIENCE IN THE ERA OF HYBRID THREATS AND THE IMPORTANCE OF A MARITIME SECURITY STRATEGY. academia.edu
Maritime Security Forum
[1] The most important use of neodymium is in an alloy with iron and boron to make very strong permanent magnets. This discovery, in 1983, made it possible to miniaturize many electronic devices, including cell phones, microphones, loudspeakers, and electronic musical instruments. Neodymium is a component, along with praseodymium, of didim glass. This is a special goggle glass used during glass blowing and welding. Neodymium glass is used to make lasers. They are used as laser pointers, as well as in eye surgery, cosmetic surgery and for the treatment of skin cancers. Neodymium oxide and nitrate are used as catalysts in polymerization reactions.
[2] Praseodymium alone is not remarkable as a permanent magnet material, but it is an excellent synergistic element that can enhance magnetic properties. The addition of an appropriate amount of praseodymium can effectively improve the performance of permanent magnet materials. It can improve antioxidant performance.
[3] Dysprosium is a rare earth element and has a metallic, shiny silvery luster. It is quite soft and can be processed without sparking if overheating is avoided. Dysprosium has the highest magnetic powers of the elements, especially at low temperatures.